Importance of Cyber Security Standards for an Organization.
CyberSecurity

What is Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity, on the other hand, is concerned with protecting digital assets – everything from networks to hardware and information that is processed, stored and transported by internetworked information systems.
BASIS Standing Committee on Digital Security Monthly Seminar Series .
Why Organization Need Information Security ?
Key Types of Information Technology Security
Although IT security and information security sound similar, they do refer to different types of security. Information security refers to the processes and tools designed to protect sensitive business information from invasion, whereas IT security refers to securing digital data, through computer network security .
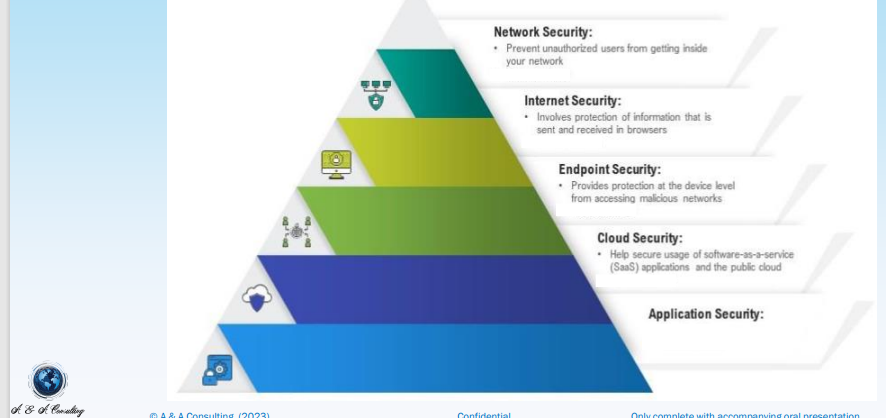
Network security : Network security is used to prevent unauthorized or malicious users from getting inside your network.
Internet security :Internet security involves the protection of information that is sent and received in browsers, as well as network security involving web-based applications.
Endpoint security :Endpoint security provides protection at the device level. Devices that may be secured by endpoint security include cell phones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers.
Cloud security : Cloud security can help secure the usage of software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications and the public cloud.
Application security : With application security applications are specifically coded at the time of their creation to be as secure as possible, to help ensure they are not vulnerable to attacks.
What are Cybersecurity Threats?
A cybersecurity threat is the threat of a malicious attack by an individual or organization attempting to gain access to a computer network, corrupt data, or steal confidential information. An information security threat is an attack that pertains directly to the IT stakeholders and your organization’s computer networks.
What Are the Top Information Security Threats?
Ransomware Remains a Persistent Threat
Supply Chain Attacks
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities, unknown to software vendors, pose significant risks. Stay vigilant for emerging zero-day threats and apply patches promptly when available.
Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing attacks, including spear-phishing, remain a common threat. Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their social engineering techniques. Keep your guard up and educate your team.
IoT Security Challenges
IoT devices are more widespread than ever, leading to new security vulnerabilities. Regularly update and secure IoT devices to prevent breaches.
Insider Threats
Insider threats can come from various sources, including employees, contractors, and business partners. Monitor and control access to sensitive data to mitigate this risk.
Insider Threats
Insider threats can come from various sources, including employees, contractors, and business partners. Monitor and control access to sensitive data to mitigate this risk.
AI and ML Attacks
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used both by cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals. Expect attackers to use these technologies for more targeted and intelligent attacks.
Cloud Security Matters
The adoption of cloud services continues to grow, making cloud security a top priority. Ensure proper configuration and robust security controls to prevent data breaches.
Nation-State Attacks
State-sponsored cyberattacks on critical infrastructure and businesses are an ongoing concern. These attacks can be highly sophisticated and pose significant risks.
Cybersecurity Regulations
Stay updated on evolving cybersecurity regulations and compliance requirements in your region. Non-compliance can lead to legal and financial consequences.
Dark Web Threats
Cybercriminals collaborate on the dark web, sharing information, tools, and services. Monitoring dark web activity related to your organization can provide valuable insights into potential threats.
Governance, Risk & Compliance
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is a structured way to align IT with business goals while managing risks and meeting all industry and government regulations. It includes tools and processes to unify an organization's governance and risk management with its technological innovation and adoption. Companies use GRC to achieve organizational goals reliably, remove uncertainty, and meet compliance requirements.
Compliance, Governance, Security and Privacy Standards.
Information Security Guidelines: • CoBit - (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) • CMMC - (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification) • FISMA - (Federal Information Security Management Act) • ISACA - (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) • ITIL - (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)

Information Security Standards for Bangladesh ICT Industry ?
What is the Information Security?
Information security deals with
information, regardless of its
format – it encompasses paper documents, digital and intellectual
property in people’s minds, and verbal or visual communications.
Information Security Standards for Bangladesh ICT
Industry
Bangladesh Bank ICT Security Guidelines
Bangladesh Digital Security Act 2018
ISO 2700X - (International Standard Organization)
PCI –DSS – (Payment Card Industry – Data Security Standard)
Information Technology Information Security Policy
Information Security Policy Document
Review of the Information Security Policy
Information Technology Information Security Policy
Information Technology Compliance with Legal Requirements
Compliance with Security Policies and Standards?
Organization of Information Security
Information security management is the process of protecting an organization's data and assets against potential threats. One of the primary goals of these processes is to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and availability